Protein Tumor Markers
Stefan PellenzBiomarkers are defined as “any substance, structure, or process that can be measured in the body or its products and influence or predict the incidence of outcome or disease”1. Certain physiological conditions are characterized by the presence or altered levels of substances specific for that condition. Substances such as proteins and peptides can be readily measured and are therefore often times used as biomarkers.
Biomarkers in tumor diagnostics
Tumor markers represent a subset of biomarkers that are indicative for cancerous growth. Most of these marker are being produced by both normal cells as well as tumor cells. The levels at which they are present in bodily fluids like urine, saliva or blood are however typically significantly higher in patients with various malignancies.
There is a plethora of tumor markers being used which can be classified base on their function, the way they are detected, or the kind of sample in which they are measured:
- Oncofetal antigens
- Tumor associated antigens
- Hormones and hormone receptors
- Enzymes and isoenzymes
- Serum and tissue proteins
- Cancer stem cells4
- other tumor markers such genetic markers and biomolecules.
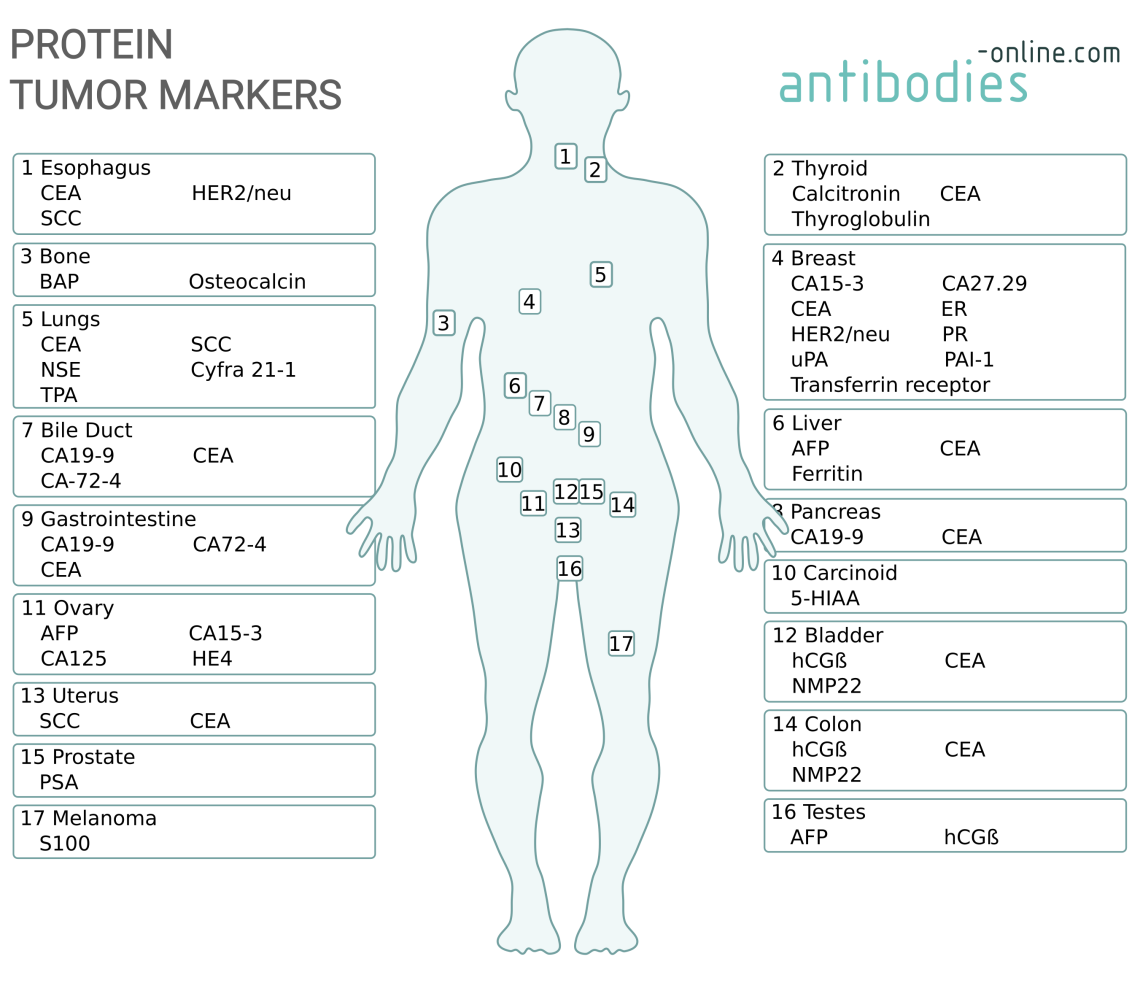
Protein Tumor Markers and their sites.
Get our Protein Tumor Marker poster!
By clicking on the link below, you can download a copy of our Protein Tumor Marker poster in PDF format.
Download a CopyA perfect tumor marker is highly specific and differentiates reliably between healthy individuals and cancer patients. It can be a universal tumor marker or specific for one particular malignancy. It should permit early detection of early stage tumors and at the same time distinguish tumor stages and have prognostic value for outcome and potential recurrence. Lastly, it should be easily measureable with established techniques to follow any changes during the course of a treatment.
None of the established markers fulfill all the points in the wish list for the perfect tumor marker. Instead, several markers are typically used in conjunction to allow for a reliable diagnosis, prognosis, staging and monitoring of a wide range of different cancer types5.
How are Tumor Markers measured?
The majority of tumor biomarkers are proteins or peptides. Consequently, they can be qualitatively and quantitatively measured using immunological methods such as ELISA, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, or other methods depending on the nature of the marker and of the sample.
An increasing number of tumor markers are also based on genetic variations6. Altered expression patterns and mutations in certain oncogenes do not affect the type of malignancy but are also determinants for the response to treatment.
Protein Tumor Markers in different Tissues
Protein Tumor Markers and their sites.

Get our Protein Tumor Marker poster!
By clicking on the link below, you can download a copy of our Protein Tumor Marker poster in PDF format.
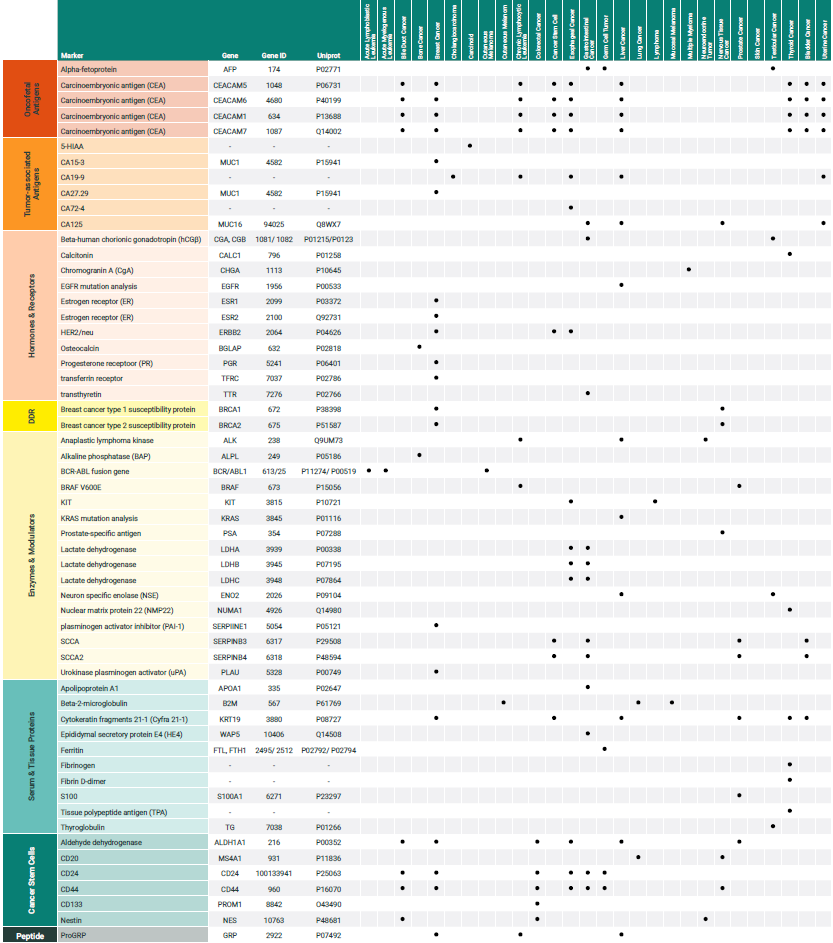
Download a CopyThe table above compiles a number of protein and peptide markers that are typically used to diagnose and monitor various malignant conditions. The first column classifies the different markers as oncofetal antigens, tumor associated antigens, hormones and hormone receptors , iso-/enzymes, serum and tissue markers, and cancer stem cell markers. The matrix indicates for which cancer types the different markers can be used.
Protein Tumor Markers Antibodies
antibodies-online offers a wide range of products relevant for immunoassays focused on commonly used tumor markers:
| Marker class | Marker | Gene | Cancer type |
| Oncofetal antigens | alpha-Fetoprotein | AFP | liver, germ cell tumors, ovarian, testicular |
| Oncofetal antigens | CEACAM5 | CEACAM5 | esophageal, bile duct, colorectal, breast, thyroid |
| Oncofetal antigens | CEACAM5 | CEACAM6 | esophageal, bile duct, colorectal, breast, thyroid |
| Oncofetal antigens | CEACAM1 | CEACAM1 | esophageal, bile duct, colorectal, breast, thyroid |
| Oncofetal antigens | CEACAM7 | esophageal, bile duct, colorectal, breast, thyroid | |
| Tumor associated antigens | Mucin 1 | MUC1 | breast |
| Tumor associated antigens | TAG-72 | - | bile duct, gastric cancer |
| Tumor associated antigens | - | carcinoid | |
| Tumor associated antigens | CA125 | MUC16 | germ cell tumors, lung, OC, uterine |
| Tumor associated antigens | CA15-3 | MUC1 | breast |
| Tumor associated antigens | - | cholangiocarcinoma, colorectal, gastrointestinal, lung, uterine | |
| Tumor associated antigens | - | gastrointestinal | |
| Hormes and receptors | CGB | CGB | choriocarcinoma, testicular |
| Hormes and receptors | Calcitonin | Calca | medullary thyroid cancer |
| Hormes and receptors | CHGA | CHGA | neuroendocrine tumors |
| Hormes and receptors | PGR | PGR | breast |
| Hormes and receptors | Transthyretin | TTR | ovarian |
| Hormes and receptors | Calcitonin | Calca | thyroid |
| Hormes and receptors | EGFR mutation analysis | EGFR | lung |
| Hormes and receptors | ESR1 | breast | |
| Hormes and receptors | Estrogen receptor (ER) | ESR2 | breast |
| Hormes and receptors | HER2/neu | ERBB2 | breast, esopahgeal, gastrointestinal |
| Hormes and receptors | Osteocalcin | BGLAP | bone |
| Hormes and receptors | Transferrin receptor | TFRC | breast |
| Hormes and receptors | Transthyretin | TTR | germ cell tumors |
| Enzymes and modulators | Alkaline Phosphatase | ALPL | bone |
| Enzymes and modulators | C-Abl Oncogene 1 | BCR/ABL1 | chronic myelogenous leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia |
| Enzymes and modulators | Prostate Specific Antigen | PSA | prostate |
| Enzymes and modulators | Lactate Dehydrogenase A | LDHA | germ cell tumors, gastric |
| Enzymes and modulators | Lactate Dehydrogenase B | LDHB | germ cell tumors, gastric |
| Enzymes and modulators | Lactate Dehydrogenase C | LDHC | germ cell tumors, gastric |
| Enzymes and modulators | SERPINB3 | SERPINB3 | esopahgeal, lung, ovarian, squamous cell carcinoma |
| Enzymes and modulators | SERPINB4 | SERPINB4 | esopahgeal, lung, ovarian, squamous cell carcinoma |
| Enzymes and modulators | Plasminogen Activator, Urokinase | PLAU | breast |
| Enzymes and modulators | BRAF V600E | BRAF | colorectal, skin |
| Enzymes and modulators | KIT | KIT | gastrointestinal, mucosal melanoma |
| Enzymes and modulators | KRAS mutation analysis | KRAS | lung |
| Enzymes and modulators | Neuron specific enolase (NSE) | ENO2 | lung, thyroid |
| Enzymes and modulators | Nuclear matrix protein 22 (NMP22) | NUMA1 | UBC |
| Enzymes and modulators | plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) | SERPINE1 | breast |
| Serum and tissue proteins | CYFRA21.1 | KRT19 | breast, lung |
| Serum and tissue proteins | WFDC2 | WAP5 | ovarian |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Apolipoprotein A1 | APOA1 | germ cell tumors |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Beta-2-microglobulin | B2M | chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Cytokeratin fragments 21-1 (Cyfra 21-1) | KRT19 | breast, esopahgeal, lung, skin, UBC, uterine |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Ferritin | FTL, FTH1 | liver |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Fibrin D-dimer | - | UBC |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Fibrinogen | - | UBC |
| Serum and tissue proteins | S100 | S100A1 | skin |
| Serum and tissue proteins | Thyroglobulin | TG | thyroid |
| Serum and tissue proteins | - | UBC | |
| Cancer stem cells | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH1A1 | bile duct, breast, gastrointestinal, lung, skin |
| Cancer stem cells | MS4A1 | cancer stem cells, lymphoma, prostate | |
| Cancer stem cells | CD24 | CD24 | bile duct, breast, cancer stem cells, gastrointestinal, germ cell tumors, liver |
| Cancer stem cells | CD44 | CD44 | bile duct, breast, cancer stem cells, gastrointestinal, germ cell tumors, liver, prostate |
| Cancer stem cells | Nestin | NES | bile duct, cancer stem cells, nervous tissue |
| Oncofetal antigens | Alpha-fetoprotein | AFP | germ cell tumors, liver, testicular |
References
- : "Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer." in: Lung cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands), Vol. 76, Issue 2, pp. 138-43, (2012) (PubMed).
- : "Genomic EWS-FLI1 fusion sequences in Ewing sarcoma resemble breakpoint characteristics of immature lymphoid malignancies." in: PloS one, Vol. 8, Issue 2, pp. e56408, (2013) (PubMed).
- : "Cancer stem cells: the challenges ahead." in: Nature cell biology, Vol. 15, Issue 4, pp. 338-44, (2013) (PubMed).
- : "Wnt signaling in cancer." in: Oncogene, Vol. 36, Issue 11, pp. 1461-1473, (2017) (PubMed).
- : "PIVKA-II is a useful tool for diagnostic characterization of ultrasound-detected liver nodules in cirrhotic patients." in: Medicine, Vol. 96, Issue 26, pp. e7266, (2017) (PubMed).
- : "Pro-gastrin-releasing peptide (ProGRP) as a biomarker in small-cell lung cancer diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation of treatment response." in: Lung Cancer (Auckland, N.Z.), Vol. 8, pp. 231-240, (2017) (PubMed).
- : "Warburg and Krebs and related effects in cancer." in: Expert reviews in molecular medicine, Vol. 21, pp. e4, (2020) (PubMed).
- : "Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer." in: Frontiers in oncology, Vol. 9, pp. 1370, (2019) (PubMed).
- : "Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions." in: Cancer discovery, Vol. 12, Issue 1, pp. 31-46, (2022) (PubMed).
- : "Cancer proteogenomics: current impact and future prospects." in: Nature reviews. Cancer, Vol. 22, Issue 5, pp. 298-313, (2022) (PubMed).
- : "The use of single-cell multi-omics in immuno-oncology." in: Nature communications, Vol. 13, Issue 1, pp. 2728, (2022) (PubMed).
- : "Claudin18.2 is a novel molecular biomarker for tumor-targeted immunotherapy." in: Biomarker research, Vol. 10, Issue 1, pp. 38, (2022) (PubMed).
- : "The role and mechanism of claudins in cancer." in: Frontiers in oncology, Vol. 12, pp. 1051497, (2022) (PubMed).
Additional References
- National Cancer Institute - Tumor Markers. Internet: http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/diagnosis-staging/diagnosis/tumor-markers-fact-sheet




