SARS-CoV-2 Cytokine Storm
In most patients developing severe COVID-19, inflammatory processes do not subside. Instead, a cytokine storm emerges, a hyper-inflammatory response involving the dysregulated activation of a large number of immune and inflammatory cells.
IL-6 levels continue to increase and the levels of IL- 2, IL-7, IL-10, TNF-α, G-CSF, CXCL10, CCL2, and CCL3 are also substantially higher in COVID-19 patients. CD4+ and CD8+ T cell numbers are anti-proportional to the levels of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-10 in COVID-19 patients. Expression of the exhaustion markers PD-1 and HAVCR2 are also increased in these cells.On the other hand, in severe cases of COVID-19 numbers of CD14+CD16+ inflammatory monocytes are increased in peripheral blood. CD14+CD16+ monocytes have also been linked to Kawasaki Disease, a rare acute inflammatory disease of the arteries in young children that has been observed in conjunction with COVID-19 recently. These CD14+CD16+ monocytes are also CD11b+ , CD14+ , CD16+ , CD68+ , CD80+ , CD163+ , CD206+ and secrete IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-alpha, thus further contributing to inflammation.
All these factors contribute to the development of a cytokine release syndrome or cytokine storm, an excessive inflammatory reaction in which cytokines are rapidly produced in large amount in response to an infection. Cytokine storm is considered an important contributor to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS).
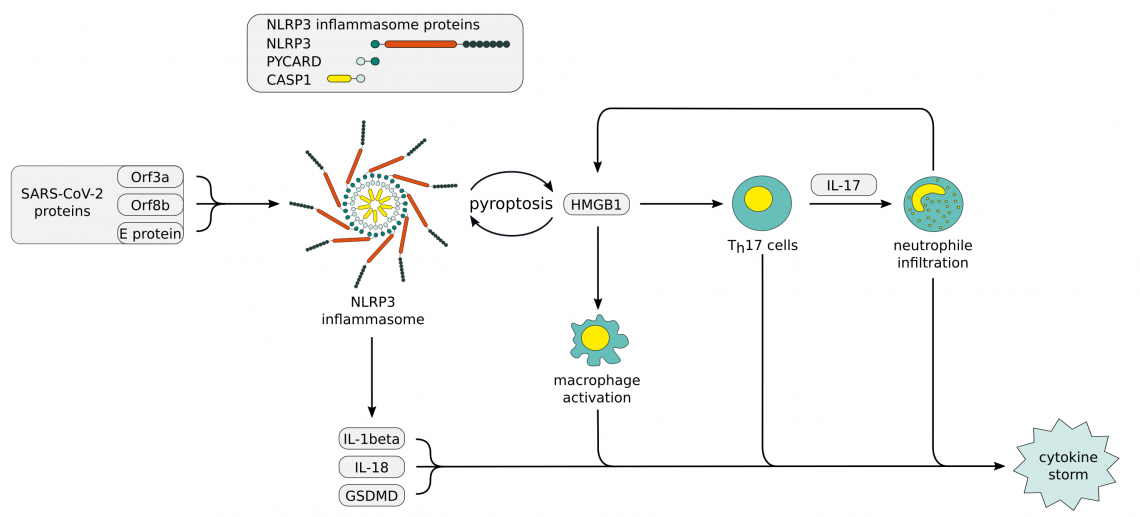
Evidence suggests an increased susceptibility to a severe course of COVID-19 due to life style related low-grade inflammation or genetics. These factors can lead to enhanced exposure to damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and further NLRP3 inflammasome activation. One of the DAMPs downstream of NLRP3 inflammasome activation is HMGB1. It is typically found in elevated serum concentrations during inflammatory events and acts as a central mediator of an excessive inflammatory response in case of viral infections. HMGB1 has been proposed to be one of the main contributors to the cytokine storm through a positive feedback loop involving induction of IL-17 production by Th17 cells and the subsequent neutrophil infiltration, leading to further NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
The SARS-CoV-2 N protein triggers activation of the lectin pathway of the complement system through interaction with mannose binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine protease (MASP)2. Released soluble N protein dimers interact with MASP-2, further accelerating MASP-2 activation and activation of the complements system. The positive feedback through cell lysis and release of N-protein leads to further increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines and aggravation of the cytokine storm.
In addition to the damaging effect on the alveolar structure, inflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF induce increases expression of HA-synthase-2 (HAS2) in CD31+ endothelium, EpCAM+ lung alveolar epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. HAS2 catalyzes polymerization of hyaluronan, a component of the extracellular matrix that can absorb water up to a 1000 times its weight. Accumulation of this liquid jelly in the damaged lungs further limits the gas exchange in the lung, leading to low oxygen saturation of the blood.

Get our free SARS-CoV-2 Handbook now!
49 Pages Handbook * Free Download * Antibodies and Proteins * SARS-CoV-2 Lineages * Mutations & Implications for NAbs
Show moreCytokine Storm related Antibodies:
- (1)
- (7)
- (2)
- (7)
- (2)
- (6)
- (8)
- (5)
- (2)
- (5)
- (8)
- (3)
- (2)
- (2)
- (1)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (2)
Cytokine Storm related ELISA Kits:
(Pre-coated)
- (53)
- (6)
(Pre-coated)
- (25)
- (6)
(Pre-coated)
- (31)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (16)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (4)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (8)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (3)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (4)
- (4)
Other COVID-19 DAMPs
The host's immune response to a SARS-CoV-2 infection is also determined by DAMPs other than HMGB1. These can be host-derived endogenous molecules that are released upon cell-death, injury-modified extracellular matrix components, or DAMP-inducible secreted proteins that downstream serve as DAMPs themselves. Besides HMGB1, DAMPs indicative of COVID-19 are CIRBP, S100A8/A9, and SP-A.
SARS-CoV-2 DAMPs antibodies:
- (4)
- (12)
- (1)
- (3)
- (2)
SARS-CoV-2 DAMPs ELISA Kits:
(Pre-coated)
- (53)
- (6)
(Pre-coated)
- (6)
- (6)
(Pre-coated)
- (4)
- (5)
(Pre-coated)
- (10)
- (1)
(Pre-coated)
- (1)
Related Information and Products
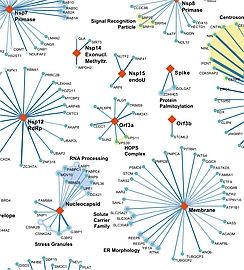
SARS-CoV Protein Interactome / poster and products
NLRP3 inflammasome, poster and products
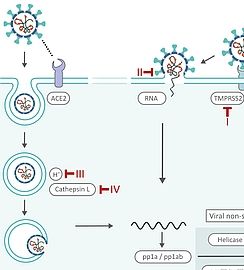
SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: Stages and Inhibition Targets
Coronavirus Expression Vectors and Cloning Vectors at genomics-online.com.
References
: "Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19." in: Cell, Vol. 181, Issue 5, pp. 1036-1045.e9, (2020) (PubMed).: "ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway." in: iScience, Vol. 24, Issue 4, pp. 102293, (2021) (PubMed).
: "The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention." in: Nature reviews. Immunology, Vol. 20, Issue 6, pp. 363-374, (2020) (PubMed).
: "Severe COVID-19: NLRP3 Inflammasome Dysregulated." in: Frontiers in immunology, Vol. 11, pp. 1580, (2020) (PubMed).
: "The CD14+ CD16+ blood monocytes: their role in infection and inflammation." in: Journal of leukocyte biology, Vol. 81, Issue 3, pp. 584-92, (2007) (PubMed).
- Gao, T. et al. Highly pathogenic coronavirus N protein aggravates lung injury by MASP-2- mediated complement over-activation. medRxiv (2020). doi:10.1101/2020.03.29.20041962
- Fan, X. et al. Changes of Damage Associated Molecular Patterns in COVID-19 Patients. Infectious Diseaeses & Immunity (2021). doi:10.1097/01.id9.0000733572.40970.6c
- Zhang, D. et al. COVID-19 infection induces readily detectable morphological and inflammation-related phenotypic changes in peripheral blood monocytes, the severity of which correlate with patient outcome. medRxiv (2020). doi:10.1101/2020.03.24.20042655